
"A" type products are the most commonly sold and loaded onto trucks or shipped. The layout of an efficient and well planned warehouse may use several logistics techniques one of the most common is ABC warehouse methodology which divides products to be shipped into three categories: A, B and C products. A few of the areas where this rule applies are listed below. This principle can provide a starting point and economical problem/issue resolution approach of the most common problems in a production plant, business or process. In all these cases 80% of the issues, plant throughput, deviations, and sales volumes are in most cases caused by only approximately 20% of the product range, possible causes, or faults. The Pareto principle can be observed and is applied in some lean concepts and operations management tools such as ABC Warehousing, production downtime, production planning, statistical quality control, supply chain design and other operations management areas.

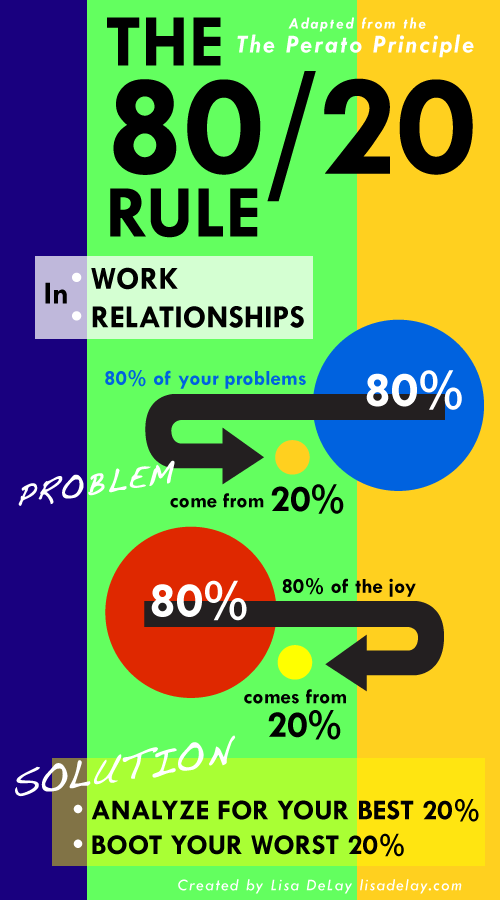
Pareto Principle in Operations Management For example in many cases 80% of business revenue is usually achieved through only 20% of products or 80% of problems in a process such as waste or production downtime are caused by only 20% of the causes. This principle has been widely observed in business and around socio economic issues in many industries and parts of the world. The pareto principle is also referred to as the 80-20 rule.įor those not familiar with the Pareto principle, it states that 80% of effects or consequences are the result of only 20% of causes. The application of the Pareto principle in problem solving and analysis can provide a great starting point with simple data analysis of process, plant failure or production data to provide an early insight into problem causes and effects without intense or complex analysis. Pareto Principle - Application in Problem Analysis and Operations Management Pareto problem analysis and pareto charts are based on the Pareto principle which is named after Italian economist Vilfredo Pareto.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
